There is one interesting thing that many Product Managers encounter in their careers. It is a constant inner tension. At least for me, when I first encountered it, it was a tough one to swallow. It made me feel ambivalent.
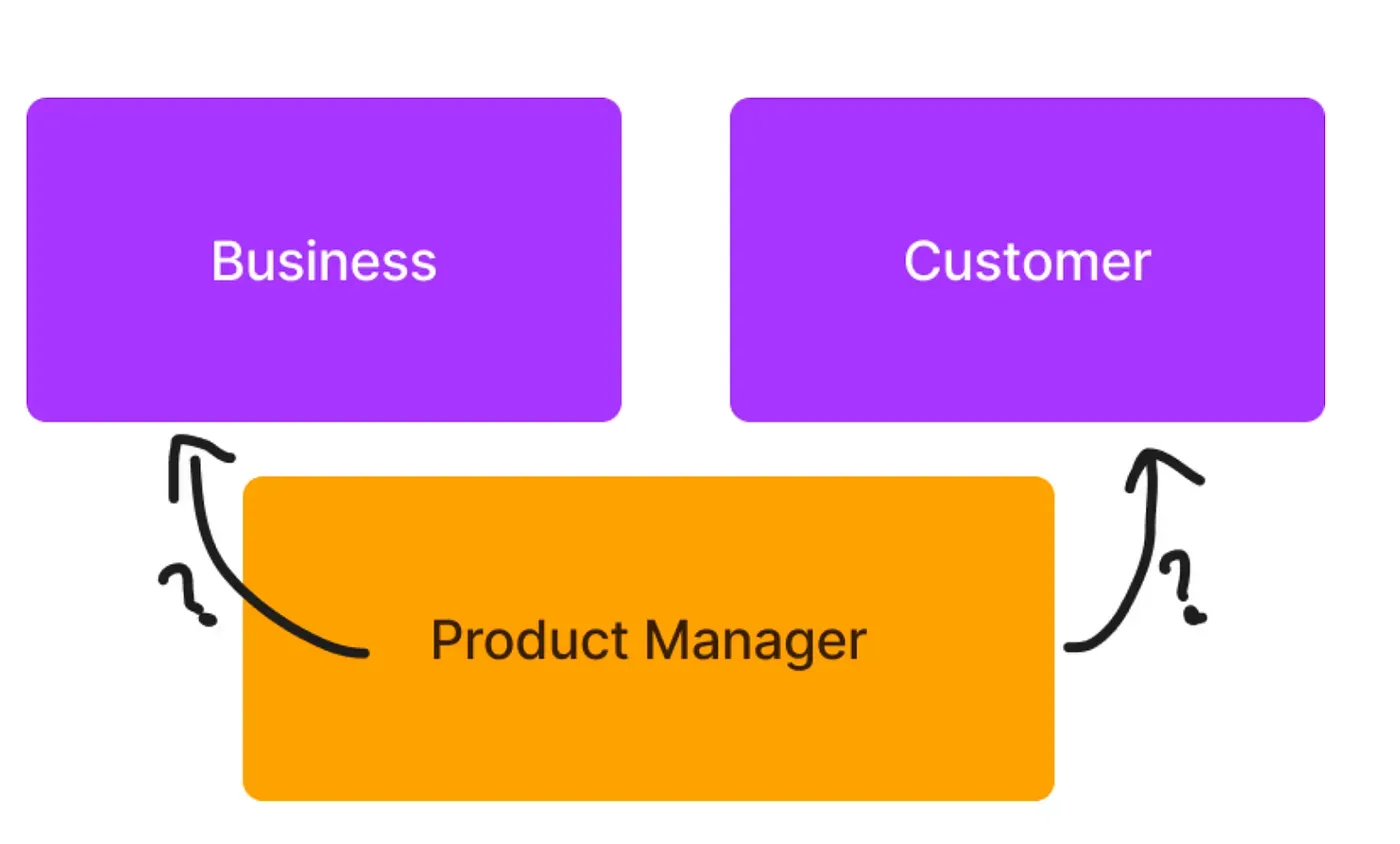
And that is… Who am I building the product for? Is it for the customer or is it for the business?
a fundamental question often arises: Who is the primary beneficiary of the product — the customer or the business?
Example: should the newspaper focus on delivering news on the first page or should it focus on placing an ad on the first page

The Customer-Centric Approach
Traditionally, product managers have emphasized the importance of meeting customer demands. In a customer-centric model, the primary goal is to identify and address the needs, preferences, and pain points of the target audience. This approach prioritizes customer satisfaction, loyalty, and retention as the key metrics of success.
Understanding Customer Needs
Central to the customer-centric approach is a profound understanding of the target market. Through market research, surveys, feedback mechanisms, and data analytics, businesses strive to gain insights into customer behavior, preferences, and expectations. By aligning product features and functionalities with these insights, product managers can create solutions that resonate with their company’s audience.
Benefits of a Customer-Centric Approach
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Products tailored to customer needs result in higher satisfaction levels, fostering loyalty and positive word-of-mouth.
- Increased Market Share: By offering superior solutions, businesses can outperform competitors and capture a larger share of the market.
- Iterative Improvement: Continuous feedback loops enable companies to refine their products iteratively, ensuring they remain relevant and competitive.
The Business-Centric Approach
Contrary to the customer-centric philosophy, the business-centric approach places greater emphasis on aligning product development with the strategic objectives of the company. Here, the primary goal is to drive profitability, efficiency, and sustainability, often through initiatives such as cost reduction, revenue maximization, or market expansion.
Prioritizing Business Objectives
In a business-centric model, product decisions are driven by considerations such as ROI (Return on Investment), profit margins, scalability, and long-term viability. While customer needs remain essential, they are weighed against the overarching goals of the organization.
Benefits of a Business-Centric Approach
- Profit Maximization: By focusing on revenue generation and cost optimization, businesses can maximize their profitability.
- Strategic Alignment: Products are developed in alignment with the broader strategic vision of the company, ensuring coherence and synergy across different functions.
- Sustainable Growth: Prioritizing business objectives facilitates sustainable growth, enabling companies to weather market fluctuations and economic challenges.
Striking the Right Balance
While the dichotomy between customer-centric and business-centric approaches may seem stark, the reality is often more nuanced. Successful product development requires striking a delicate balance between meeting customer needs and achieving business objectives. Here are some strategies for achieving this equilibrium:
- Market Segmentation: Identify different customer segments and tailor products to meet the unique needs of each group while ensuring alignment with business goals.
- Value Proposition: Craft a value proposition that resonates with customers while delivering tangible benefits to the business, such as increased revenue or reduced costs.
- Feedback Loops: Establish robust feedback mechanisms to gather insights from customers and incorporate them into product development processes without losing sight of strategic priorities.
- Iterative Approach: Adopt an iterative approach to product development, allowing for continuous refinement based on evolving customer preferences and market dynamics.
Conclusion
In the complex landscape of product development, the question of whom the product is built for — the customer or the business — is not easily answered. Its a constant inner tension for the product managers. Ultimately, successful products are those that strike a harmonious balance between serving customer needs and fulfilling business objectives. By embracing a holistic approach that integrates customer-centricity with strategic foresight, product managers can create products that resonate with their audience while driving sustainable growth and profitability.